Deep Vein Thrombosis treatment includes medication, medical procedures, and the use of compression stockings, but before heading to the treatment, let’s learn all about the condition. DVT is a serious condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in the veins located deep inside your body. DVT itself is not life-threatening; however, if left untreated, it could progress and cause complications that can be fatal. Therefore, this condition must be taken care of as soon as one notices it. That’s why if you think you may have DVT, you must see a doctor right away.
Before we talk about deep vein thrombosis treatment and DVT diagnosis, we must know more about the condition and its causes, along with DVT symptoms and signs. It is also critical to be aware of the proactive measures that one can take to prevent the disorder from occurring, especially since it can have fatal complications.
What is DVT and Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment?
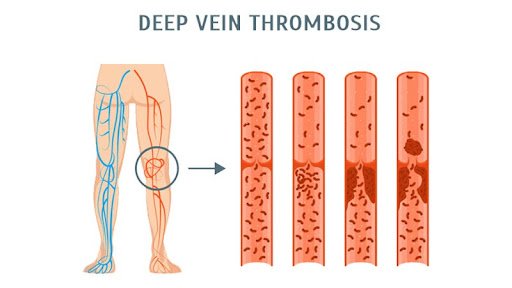
A DVT is a blood clot that occurs in deep veins of the body, the most common sites for these to occur are in the legs, thigh, or hips. It can also form in deep veins within your arms; however, this is rare.
These blood clots are clumps of blood that turn from liquid to solid or gel-like states. If these clots are not attended with immediate effect, they can block the blood flow back to the heart. If this clot, or a part of it, breaks free, moves through the bloodstream, and gets stuck in the lungs, it can become fatal. This is called Pulmonary Embolism and is a very critical complication of DVT. So it’s important to address the condition and get yourself checked if you think you are facing any similar issues.
Before we move on to the Deep Vein thrombosis treatment, let’s get to know the causes and symptoms of DVT in the legs and the risk factors involved.
What Are The Causes Of DVT In Legs?
There are several factors associated with the causes and occurrence of DVT. The primary source for this venous condition is damaged veins and the incorrect flow or clotting of blood in the veins. So, taking appropriate steps to encourage smooth blood circulation and prevent blood clots from occurring in the first place would be the ideal course of action. Let’s see the factors that could lead to the formation of blood clots.
Risk Factors
- Age (60 years and above) Although DVT can occur at any age, with age risk of developing DVT increases
- Family history of developing blood clots
- Any previous injury in the deep veins
- Major surgery such as hip or knee replacement
- Pregnancy (due to changes occurring in the body as it prepares for the growing baby)
- Birth control pills and hormonal imbalance (research indicates that there is an increased risk of developing blood clots associated with consuming some types of estrogen-containing oral contraceptive pills as well as menopause)
- Bedridden due to an injury or surgery
- Cancer or cancer treatments
- Smoking cigarettes can slow down the blood circulation
- Obesity or overweight
- Standing or sitting for long periods
Preventive Measures For Deep Vein Thrombosis
Taking a few measures to prevent DVT is always a good idea in the long run. This is especially important for people at a greater risk of developing the condition due to pregnancy, genetic predisposition, frequent traveling, prolonged bed rest, thrombophilia, et cetera.
Today, we will tell you the measures you can take to prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis and lead a healthier and pain-free life.
1) Consider DVT Stockings To Encourage Healthy Blood Circulation
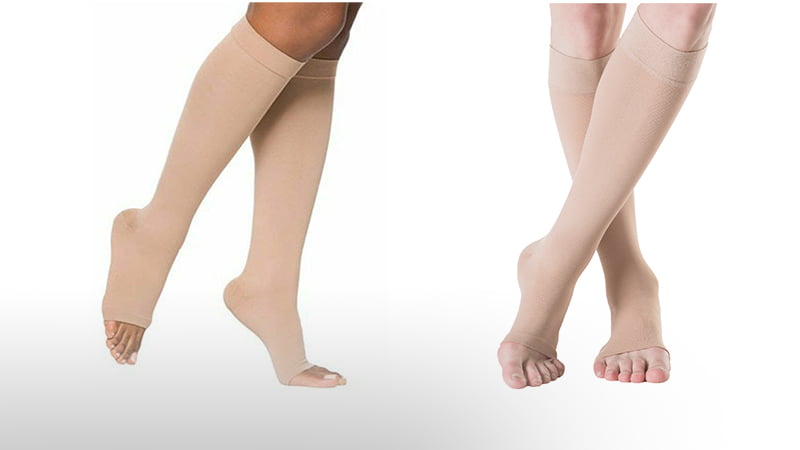
Compression stockings are one of the most practical measures you can take to prevent blood clots and, thus, the prevention of pulmonary embolism. Compression stockings are found in 2 lengths that are knee-length and thigh-length. These stockings apply graduated compression to the leg to ensure a better flow of blood throughout your legs. So, buy your graduated DVT stockings from Novomedshop to get the best quality and functionality.
The stockings are available in different levels of compressions based on the patient’s underlying condition and need. However, it is important to check with your doctor for the type and compression level you may need.
2) Exercise Regularly to keep venous disorders away
Exercising regularly helps keep you active and assists in the efficient circulation of blood throughout your body. Even a low-impact activity such as walking regularly can significantly help lower the risks of Deep Vein Thrombosis and help you live a healthier life.
3) Change your body positions or move around often
Avoid staying still for long hours, be it sitting or standing. Instead, take a break now and then and relax your legs by moving around frequently. Elevate your legs often to reverse the impact of gravity and ensure healthy blood flow.
4) Stay hydrated to prevent blood from thickening
Dehydration could cause blood to thicken and flow slowly. Ensure that your fluid intake is in place to reduce the viscosity of blood. Also, alcohol and large quantities of caffeinated beverages can add to the risk of dehydration.
5) Pregnancy care to avoid DVT and other venous insufficiencies
If you are expecting, speak to your doctor to assess your risk of developing DVT symptoms and signs and follow their advice diligently. This is essential as the risk of developing DVT is 5 times higher during pregnancy and 50 times higher post-partum. Appropriate care during pregnancy can avert any problems in the future.
Consult a Doctor
Suppose you already have a family history of blood clots and Thrombophilia. In that case, we suggest you consult a doctor to help you prevent the risks of developing DVT with the help of blood thinners, compression stockings, et cetera.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Symptoms And Signs

DVT may not always show symptoms, but it is supposed to be addressed on an immediate basis if they do. The symptoms of DVT in the legs usually differ from person to person. Here are some of the signs that will help you identify the condition or alert you to see a doctor and seek medical help as soon as possible.
- Swelling in the legs
- Pain and tenderness in legs
- warm skin
- Discolored skin
- Cramps in the leg
In more severe cases, one might observe the following DVT symptoms and signs:
- Coughing up blood
- Chest pains and tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid heartbeat
DVT Diagnosis
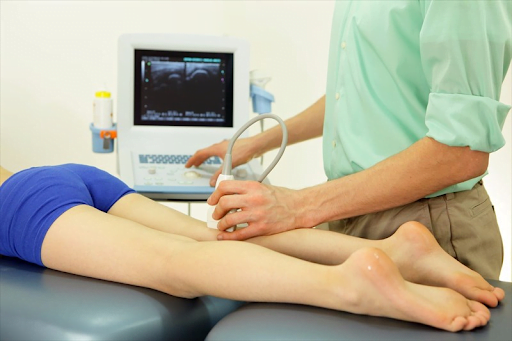
A prompt Deep Vein Diagnosis could result in the early detection of potentially life-threatening conditions like a pulmonary embolism. So, the significance of DVT diagnosis can prevent the blood clot’s progression and prove to be crucial in managing the symptoms of DVT better.
The Deep Vein Thrombosis diagnosis would require a physical exam as well as some special tests to detect if any blood clots exist in the veins. Then, depending upon the risk and the condition’s intensity, a few tests will be conducted to arrive at a conclusion and start the deep vein thrombosis treatment. Here’s a list of methods to diagnose Deep Vein Thrombosis.
Physical Exam:
Your doctor will conduct a physical exam of your limb to check for any external symptoms such as swellings, tenderness, and any change in the color of your skin.
D-Dimer blood test:
Blood clots produce a type of protein called D- dimer. Most people suffering from DVT have increased levels of D-dimer. A D-dimer test helps diagnose DVT, and a normal result helps rule out Pulmonary Embolism.
Venous Ultrasound:
An ultrasound would help track the flow of your blood with the help of sound waves. The test is conducted on various parts of your body to check for new clots.
Venography:
Venography is conducted by injecting a dye into your veins. After which, an x-ray is taken to track blood movement throughout your veins and check for clots.
MRI Scan:
A magnetic resonance imaging scan is done when ultrasound is not possible or to locate a clot in the heart. This gives precise imaging of the clots in your body and helps doctors start with the Deep Vein Thrombosis treatment.
Impedance Plethysmography:
In certain cases of Deep Vein Thrombosis Diagnosis, physicians can adopt impedance plethysmography. It is a non-invasive test procedure that is used to detect the potential presence of DVT in the legs. This particular test measures the changes in blood volume in the leg as a result of a blood clot.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment
Deep Vein Thrombosis treatment intends to dissolve the blood clot in your deep veins, prevent the clot from getting bigger, and ensure that the clot does not reoccur in the future. However, since the complications can be fatal, it is essential to start Deep Vein Thrombosis treatment as soon as possible.
Here is a list of all the possible ways to treat DVT and how they work.
Anticoagulants:
To prevent the existing clots from getting bigger and the formation of new clots, patients are prescribed anticoagulants. Anticoagulants prevent the blood from coagulation, which means thickening or clotting. Anticoagulants are also called blood thinners. These do not break down or dissolve an existing blood clot but prevent an existing clot from getting bigger and reduce the risks of developing new blood clots. Anticoagulants can be taken orally, through an IV, or an injection. There are a number of anticoagulants available for deep vein thrombosis treatment or to prevent it from worsening.
Catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT):
Catheter-directed thrombolysis is a minimally invasive procedure that breaks down the blood clot using medication. These clot-busting drugs are called Thrombolytics. They are injected directly into the clots to dissolve them quickly and restore blood flow. A catheter is inserted into your vein through the clot to execute this procedure, and then the drug is injected into the clot. The process is riskier than blood thinners and hence isn’t used by doctors until needed by the patient for deep vein thrombosis treatment in severe cases.
Vein Filter Placement:
This procedure is used only to prevent the chances of pulmonary embolism caused by DVT. Under this, a small filter is inserted into your inferior vena cava (IVC) to protect blood clots from flowing to your heart and lungs. The inferior Vena cava is the vein that sends the blood from the lower half of your body back to the heart.
Venous Thrombectomy:
Venous Thrombectomy is the removal of a blood clot from the leg vein with surgery. This procedure is done in cases where the patient has acute vein blockage and/or severe symptoms.
The Takeaway
Here we read all about the Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment, Diagnosis, Prevention, and its Symptoms. DVT symptoms and signs may appear right away or might take as long as a year to show up. Once treated, there is also a high chance of recurring. Wearing graduated DVT stockings can reduce the risk of developing any kind of venous disorder and keep your veins healthy and fit. There are several benefits of medical compression socks. Wearing these regularly, with or without any symptoms of venous insufficiency, will always keep you ahead of the curve in terms of vein health.
Deep Vein Thrombosis diagnosis and early identification and detection can minimize many complications. Blogs can educate readers on deep vein thrombosis (DVT) symptoms and diagnostic tools, which might increase the likelihood that people at risk will seek medical help quickly, which could save lives while enhancing lifestyles.


Comments
There are no comments yet.