Pulmonary embolism can be prevented entirely by taking the right precautions. The risk of developing this condition often arises from the legs and requires immediate attention to control it. To effectively manage pulmonary embolism, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of what pulmonary embolism is, how to diagnose it, how to prevent it, and pulmonary embolism treatment.
What is Pulmonary Embolism?
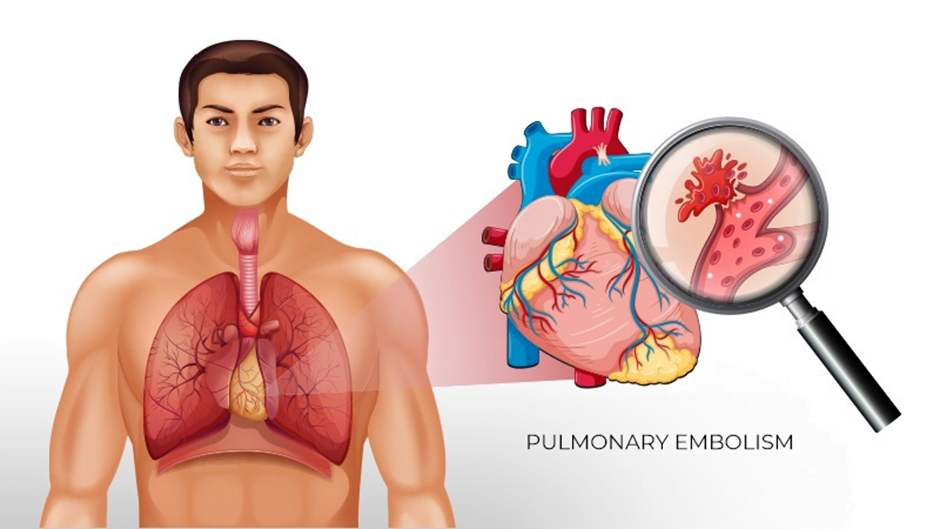
Pulmonary Embolism occurs when a blood clot blocks an artery in the lungs. This blood clot usually forms in the legs and travels up through the bloodstream. The blockage can reduce blood flow to the lungs and prevent oxygen from reaching the rest of the body, making it life-threatening. A pulmonary embolism is a medical emergency in which early diagnosis and treatment is crucial for improving positive outcomes.
How To Prevent Pulmonary Embolism?
You can take several precautions to prevent Pulmonary Embolism; even the smallest measures can make the biggest difference. If you have a family history of blood clots, we suggest you take these precautions regardless.
Preventive measures for Pulmonary Embolism
Compression stockings are very commonly recommended by doctors to patients suffering from venous conditions such as deep vein thrombosis, varicose veins and blood clots. Compression stockings support veins and improve blood circulation, thus preventing the formation of blood clots. We advise you to consult your doctor and ask them to suggest the best compression stockings for you.
Exercise Regularly:
Another great way to prevent and reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism is by exercising regularly. This would help improve blood circulation in your leg, feet, and the rest of your body.
Drinking fluids regularly:
Keep yourself well hydrated. Dehydration causes narrow blood vessels and thickens the blood, leading to increased risks of blood clots.
Avoid sitting or standing for too long:
Sitting or standing for long periods without breaks can increase the chances of blood clots and pulmonary embolism. You should walk around, relax your feet and legs and stretch every once in a while to reduce the risks of pulmonary embolism.
Pulmonary Embolism Symptoms
The symptoms of Pulmonary embolism can vary from person to person depending upon the severity of the disease and factors such as the size of the clots, underlying heart or lung-related diseases, etcetera.
Common symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism include:
- Sudden Shortness of Breath
- Sharp Chest, arm, shoulder, or neck pains stop you from taking a deep breath
- Coughing Blood
- Pale skin colour (Cyanosis)
- Dizziness
- Rapid Heartbeat
- Deep vein thrombosis
Diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism
A pulmonary embolism is usually a little difficult to diagnose, especially when it comes to lung and heart patients, yet there are a few ways through which doctors can diagnose pulmonary embolism after going through your medical history and conducting a few tests. Let’s find out some of the methods used to diagnose pulmonary embolism.
- Blood clot tests
- Chest X-Rays
- CT scan
- Ultrasound
- CT Pulmonary Angiography
- Catheter-based Pulmonary Angiography
- Echocardiogram
- MRI
Pulmonary Embolism Treatment
There are 2 types of pulmonary embolism treatments that can stop clots from getting bigger and also prevent the formation of new clots. Pulmonary embolism treatment involves medicines and surgeries. Let’s throw some light on the types of surgeries and medicines that help in the treatment of Pulmonary embolism.
Medications
- Anticoagulants: Also known as blood thinners, these medicines work towards stopping the blood clots from getting bigger and preventing the formation of new blood clots.
- Clot Dissolvers: These are injected into the veins to dissolve existing clots. This process of breaking down the clots with medication is called thrombolysis.
Surgeries
- Clot Removal: Clots can be removed surgically by the insertion of a catheter into your veins. This is usually suggested if you have a large clot that might be life-threatening.
- Vein Filter: A vein filter inserted into your inferior vena cava will prevent all clots from reaching your lungs. This treatment method is practised when the anticoagulants don’t seem to work anymore or when the patient can’t be given anticoagulants for some reason.
Well, here’s everything you need to know about Pulmonary Embolism treatment, its diagnosis, symptoms, and prevention methods. However, your doctor can be the best advisor for these delicate issues. You can find the best compression stockings as prescribed by your doctors right here to mitigate the risks of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. With the right stockings, you can reduce the risks of blood clots caused by sitting or standing for too long.


Comments
There are no comments yet.